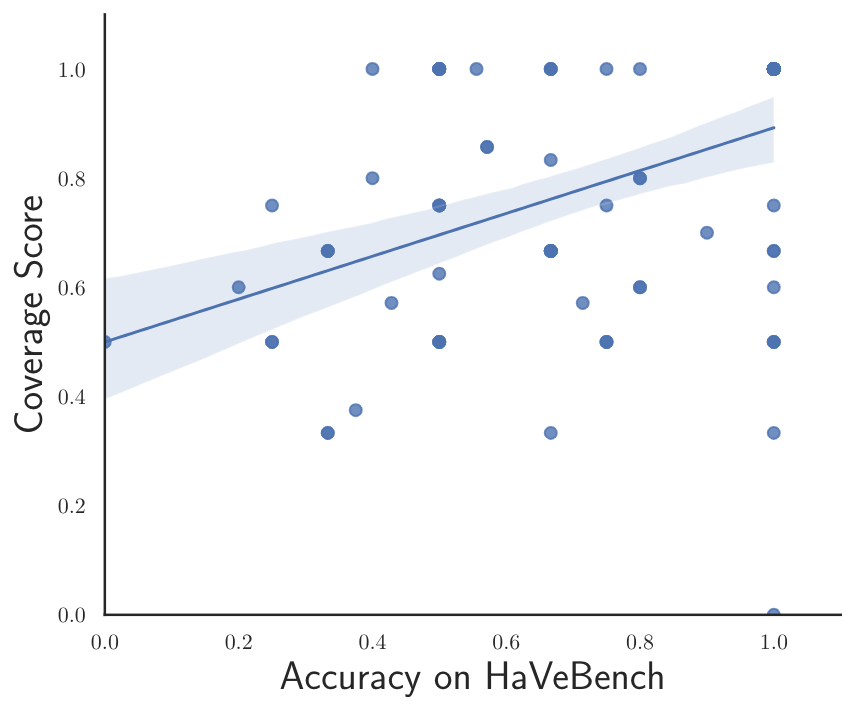
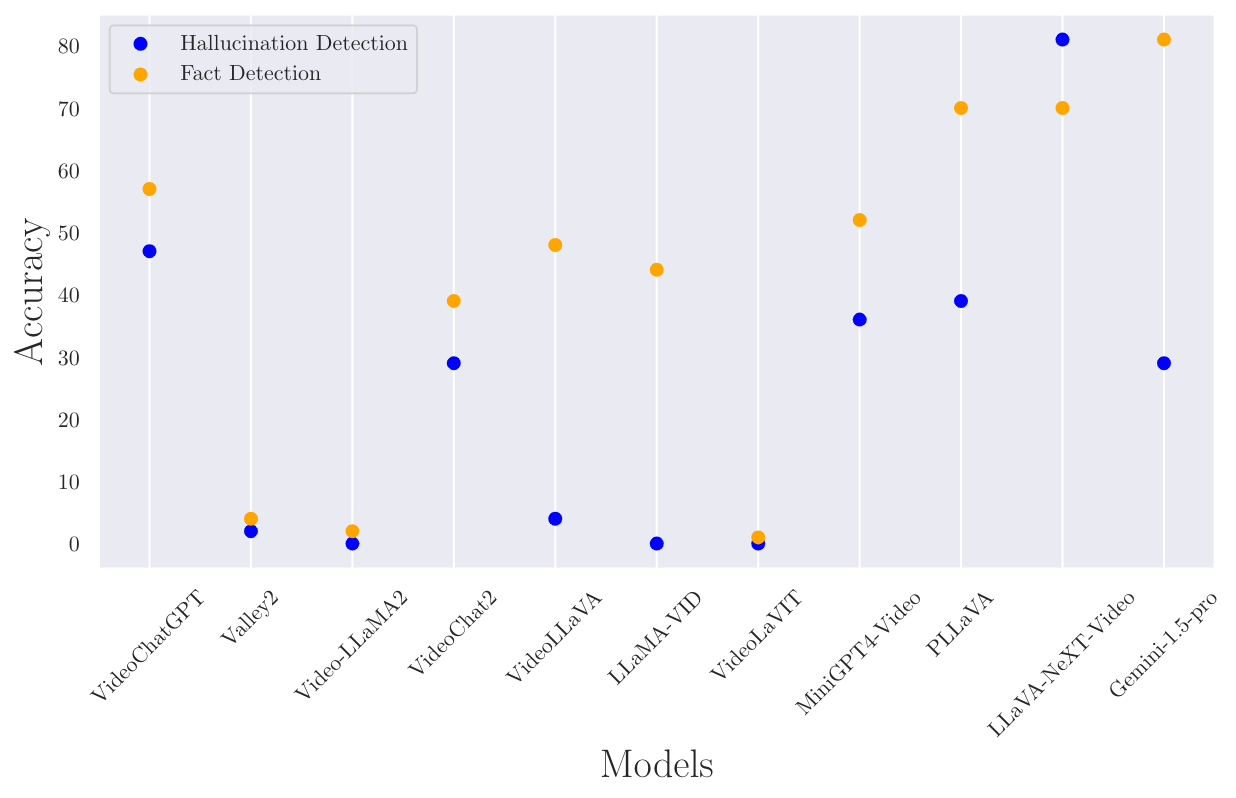
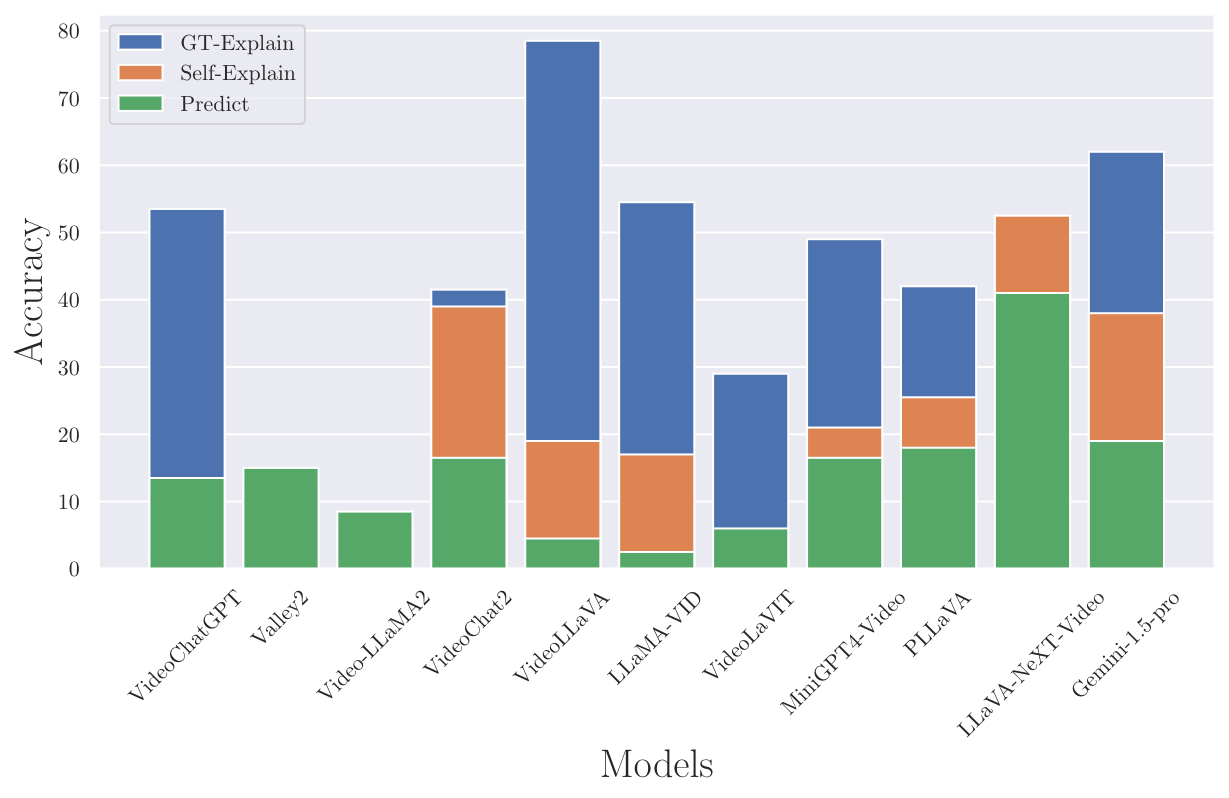
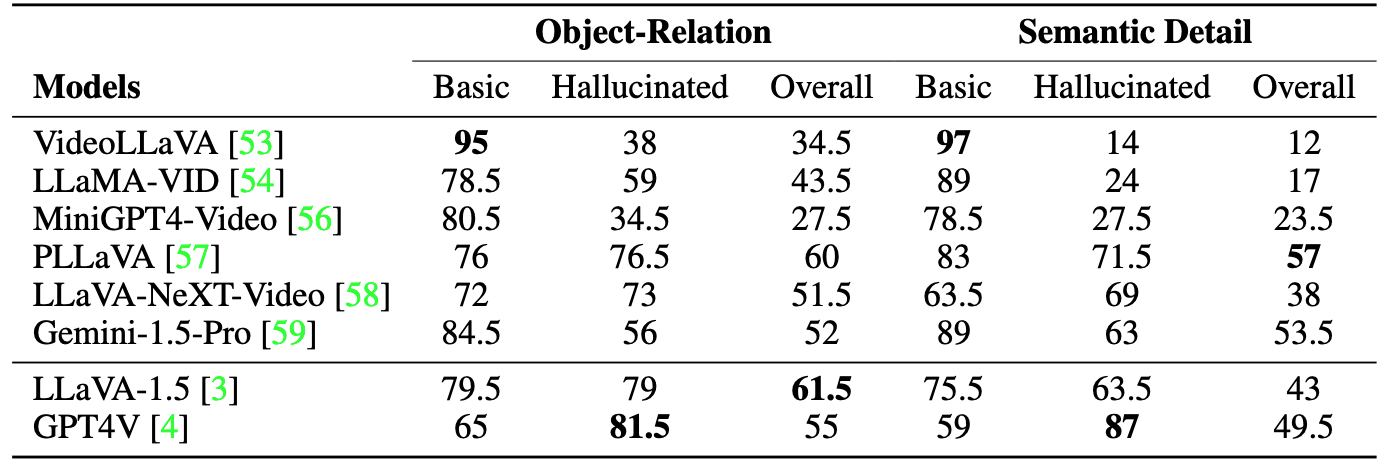
Accuracy scores on the VideoHallucer.
| # | Model | LLM | Frames | Date | Yes/No Bias | Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pct. Diff (∼ 0) | FP Ratio (∼ 0.5) | Basic | Hallucinated | Overall | |||||
| 1 | Human | - | - | 2024-05-25 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 90 | 88.8 | 85 |
| 2 | GPT-4o | - | 16 | 2024-06-18 | -0.02 | 0.43 | 75.1 | 74.2 | 53.3 |
| 3 | PLLaVA-34B | Yi-34B | 16 | 2024-05-25 | 0.18 | 0.78 | 90.8 | 50.8 | 45 |
| 4 | PLLaVA-13B | Vicuna-13B-1.5 | 16 | 2024-05-25 | 0.17 | 0.72 | 87.5 | 48.6 | 41.2 |
| 5 | PLLaVA | Vicuna-7B-1.5 | 16 | 2024-05-25 | 0.06 | 0.53 | 75.1 | 55.5 | 38.1 |
| 6 | Gemini 1.5 Pro | - | 1 fps (-128) | 2024-05-25 | 0.15 | 0.62 | 83.6 | 42.3 | 37.8 |
| 7 | LLaMA-VID-13B | Vicuna-13B-v1.5 | 1 fps | 2024-05-25 | 0.21 | 0.72 | 85.2 | 36.9 | 29.2 |
| 8 | LLaVA-NeXT-Video-DPO-34B | Yi-34B | 4 | 2024-05-25 | 0.07 | 0.55 | 73.6 | 51.6 | 32.3 |
| 9 | LLaVA-NeXT-Video-DPO | Vicuna-7B-1.5 | 4 | 2024-05-25 | -0.04 | 0.40 | 62.5 | 60.9 | 32.0 |
| 10 | MiniGPT4-Video | Mistral-7B | (-45) | 2024-05-25 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 79.4 | 28.6 | 22.3 |
| 11 | LLaMA-VID | Vicuna-7B-v1.5 | 1 fps | 2024-05-25 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 89.9 | 26.6 | 21 |
| 12 | VideoLaVIT | LLaMA2-7B | 16 | 2024-05-25 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 94.9 | 21.3 | 18.9 |
| 13 | Video-LLaVA | Vicuna-7B-v1.5 | 8 | 2024-05-25 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 95.1 | 20.3 | 17.8 |
| 14 | ShareGPT4Video | LLaMA3-8B | 16 | 2024-06-25 | 0.31 | 0.79 | 88.5 | 20.0 | 15.8 |
| 15 | Video-LLaMA2 | LLaMA2-7B | 8 | 2024-05-25 | 0.36 | 0.84 | 90.9 | 12.7 | 10 |
| 16 | VideoChat2 | Vicuna-7B-v0 | 4 | 2024-05-25 | -0.24 | 0.15 | 29.7 | 25.8 | 7.8 |
| 17 | VideoChatGPT | LLaMA-7B | 100 | 2024-05-25 | 0.40 | 0.89 | 92.8 | 10.4 | 6.4 |
| 18 | Video-LLaMA2-13B | LLaMA2-13B | 8 | 2024-05-25 | 0.36 | 0.79 | 88.3 | 3.8 | 3.3 |
| 19 | Valley2 | LLaMA2-7B | 8 | 2024-05-25 | -0.07 | 0.29 | 44.4 | 11.5 | 2.8 |
Accuracy scores on the different VideoHallucer settings.